When a cannabis plant’s roots have little room to stretch out, it gets rootbound, which commonly results in health complications. Rootbound cannabis has slow growth and may show nutrient deficiencies, discoloration, and drooping leaves. In order to maintain the plant healthy and guarantee a reasonable output, this problem must be rectified as soon as possible.
Knowing rootbound plant symptoms can help you avoid a worsening situation. Cannabis needs frequent monitoring to grow properly. Rootbound difficulties can be fully prevented by comprehending how vital it is to utilize the proper container size and transplant on time.
Key Takeaways
- Rootbound cannabis absorbs nutrients and water poorly.
- Early detection can rescue your plants.
- Proper transplanting avoids rootbound problems.
Understanding Rootbound Situations
A cannabis plant is rootbound when its root system is limited in its pot. This may result in a multitude of difficulties that influence the plant’s development and well-being. To better care for your cannabis plants, know the symptoms and causes of root-bound diseases.
What Does Rootbound Mean?
A rootbound cannabis plant has roots that are tightly packed within its pot, forming dense masses that spiral along the container walls sometimes called a root ball. This prevents the roots from absorbing water and nutrients effectively. The restricted space causes the plant to stop growing efficiently and visible stress, such as drooping leaves.
As the roots struggle to function, the soil may dry out quickly after you water your plant, further compounding the plant’s problems. Regularly checking the root system and ensuring adequate space for root expansion is crucial for maintaining healthy cannabis plants.
Causes of Rootbound Cannabis
Rootbound conditions occur for several reasons, often due to poor planning or delayed action while growing cannabis. Using a pot that’s too small for the plant’s size is a primary cause. Over time, the roots fill the limited space, leaving no room to grow.
Failure to recognize the need to transplant plants into larger containers exacerbates the issue. As cannabis plants grow, their roots naturally seek more room to spread. Additionally, poor drainage in the pot can create waterlogged conditions that stress the roots, making the plant more susceptible to becoming rootbound.
Recognizing Symptoms of Rootbound Plants
Identifying a rootbound plant involves observing physical signs and understanding the impacts on growth. Recognizing these symptoms early is key to addressing the issue effectively.
Visual Symptoms of Rootbound Plants
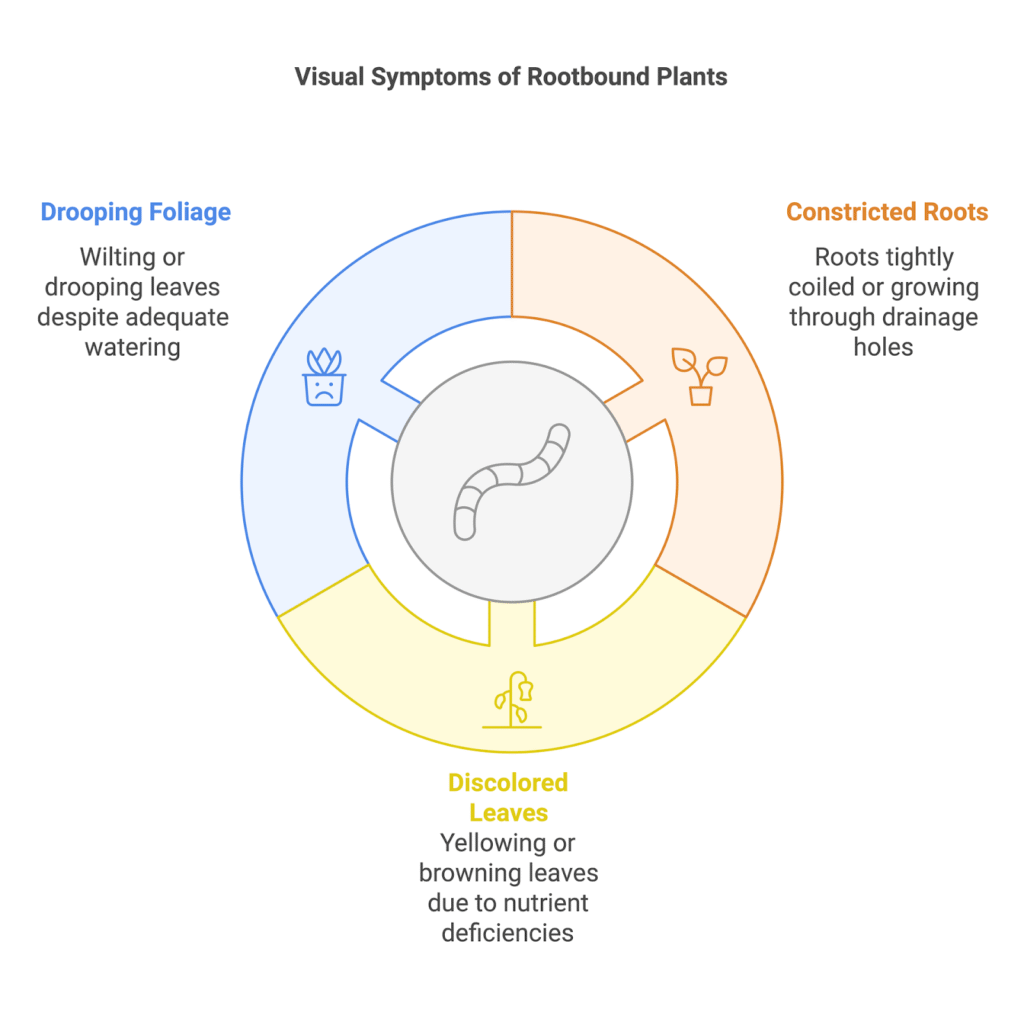
Rootbound plants exhibit distinct physical indicators:
- Constricted Roots: Roots tightly coiled at the pot’s base or growing through drainage holes signal limited space.
- Discolored Leaves: Yellowing or browning leaves, often due to nutrient deficiencies, are common.
- Drooping Foliage: Persistent wilting or drooping leaves, even after watering, indicate that roots cannot absorb moisture efficiently.
Inspect your plants regularly for these signs. Stunted or misshapen leaves may also point to rootbound conditions.
Growth and Health Impacts
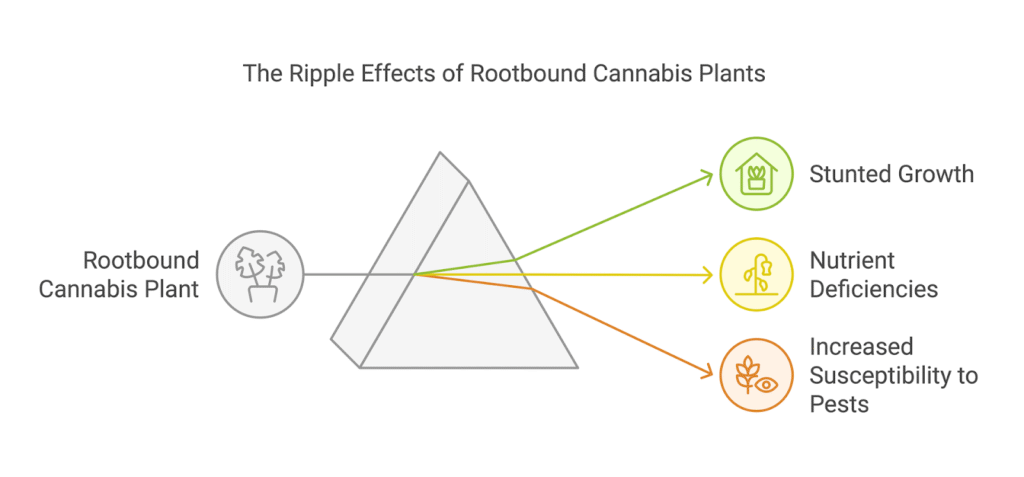
A rootbound cannabis plant faces numerous challenges:
- Stunted Growth: Limited root space prevents the plant from reaching its full size and producing a high yield.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Crowded roots struggle to absorb essential nutrients, leading to weak stems and poor leaf development.
- Increased Susceptibility to Pests: A stressed plant becomes more vulnerable to diseases and pest infestations.
By addressing these issues promptly, you can minimize damage and restore your plant’s health.
Transplanting Rootbound Cannabis Plants
Transplanting is the most effective way to rescue a rootbound cannabis plant, especially at the seedling stage. Understanding when and how to transplant ensures a smoother recovery and continued growth.
When to Transplant
Recognize the signs that it’s time to transplant:
- Roots emerging from drainage holes.
- Stunted growth despite adequate care.
- Soil that dries out quickly after watering.
Act quickly when these symptoms appear. Delayed transplanting can lead to severe root damage and declining plant health.
Steps for Transplanting
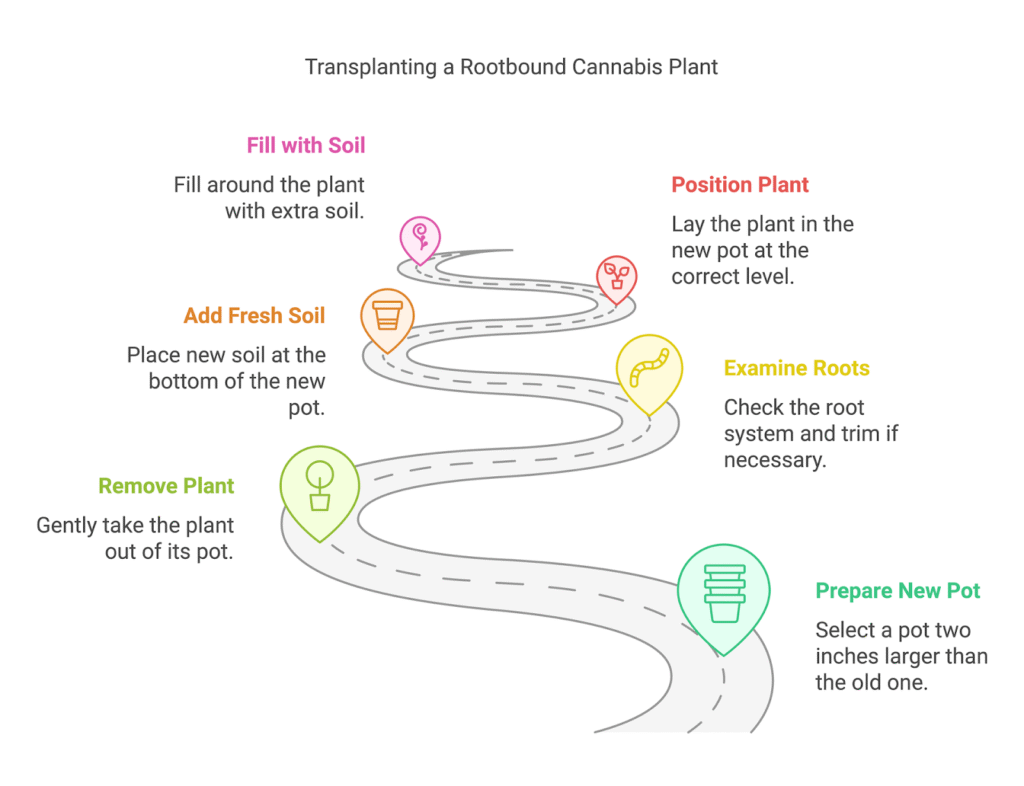
The first step in transplanting a rootbound cannabis plant is to prepare a new pot that is at least two inches bigger than the old one. For optimal growth, use nutrient-rich, high-quality soil.
- Take the Plant Out: Remove your cannabis plant gently from its pot. Loosen the edges of the soil if it’s stuck.
- Look at the Roots: Examine the root system. To promote new development, you might need to cut part of the roots if they are tightly wound.
- Add Fresh Soil: Place some new soil at the bottom of the new pot. Then, lay the plant in and fill around it with extra soil, making sure the base of the stem is level with the soil surface.
- Water Thoroughly: After the transplant, water the plant well. This helps to settle the soil and offers moisture for recovery.
To give your cannabis plant the best chance of growing healthily, please follow these instructions.
Best Practices for Healthy Cannabis Cultivation
Preventing rootbound conditions requires proper planning and consistent care. Best practices include selecting appropriate containers and maintaining root health.
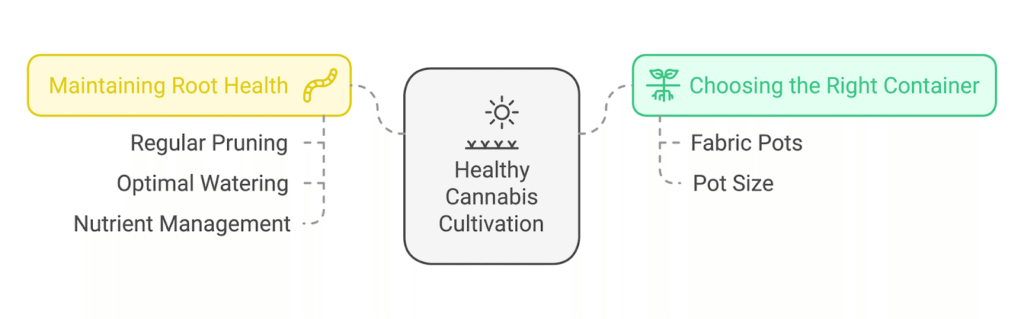
Choosing the Right Container
Fabric pots, also called smart pots, are excellent for cannabis plants as they promote air pruning and reduce the risk of rootbinding. The breathable material allows oxygen to reach the roots, encouraging outward growth.
Choose a pot size based on your plant’s expected growth. For smaller plants, one- to three-gallon pots are sufficient, while larger plants may require five gallons or more. Regularly inspect the roots to determine when a larger container is needed.
Maintaining Root Health
Healthy roots are essential for robust plant growth:
Regular Pruning: Trim dead or damaged roots to prevent tangling and encourage fresh growth.
Optimal Watering Practices: Water only when the soil is dry to the touch. Overwatering can suffocate roots and lead to rot.
Nutrient Management: Use balanced nutrient solutions to support root health and overall plant development.
Implementing these practices ensures your plants grow strong and avoid rootbound issues.
Monitoring and Preventing Rootbound Problems
Preventive measures and regular observation are critical for avoiding rootbound conditions. Addressing potential issues early will help your plants thrive.
Continuous Monitoring
Check your plants frequently for signs of stress. Inspect the roots periodically, especially as the plants grow larger. Look for roots protruding from the pot’s drainage holes or coiling at the base.
Monitor soil moisture levels and adjust watering schedules as needed. Rapid drying of the soil can indicate restricted root growth. By staying vigilant, you can catch rootbound problems before they become severe.
Proactive Prevention
Prevent rootbound conditions by:
- Choosing pots that accommodate root growth.
- Transplanting promptly when roots outgrow their containers.
- Using fabric pots to promote air pruning and healthy root systems.
Repotting regularly as plants mature helps avoid overcrowding and supports optimal growth.
Bottom Line
Rootbound conditions can hinder cannabis plant growth, but with timely intervention and proper care, these challenges can be overcome. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and solutions, you can cultivate healthier plants that thrive and produce higher yields. Stay proactive, and your cannabis plants will reward you with robust growth and abundant harvests.








