A nitrogen deficit could have detrimental effects on the output and general state of health of cannabis plants. Healthy development depends on an awareness of the indicators and sources of nitrogen deficit.
This common issue can fool even experienced gardeners and it usually causes slower development and browning of the leaves. Your cannabis plants may not be getting enough nitrogen if their bottom leaves are yellow since amino acid synthesis as well as photosynthesis rely on nitrogen.
Early identification and treatment would help with plant development and harvesting. Growing cannabis plants requires control of nitrogen levels. Correct knowledge guarantees that your plants acquire the nutrients they require and helps you avoid nutrient shortages.
Understanding Nitrogen Deficiency
Among the most prevalent difficulties harming cannabis plants are nitrogen deficiencies. Understanding how nitrogen promotes plant growth and identifying the symptoms is essential for successful cultivation.
Signs and Symptoms of a Nitrogen Shortfall
Nitrogen-deprived cannabis plants show different symptoms. The most obvious sign is older leaves—especially those near the base of the plant—turning yellow. Usually beginning at the leaf tips, the discoloration advances inside.
Other signs are stunted growth in plants, which would make them seem less healthy.
The leaves could be getting smaller, softer, and curl inward.
Lack of nitrogen can reduce the synthesis of chlorophyll, therefore compromising photosynthetic efficiency and generating further problems.
Early discovery of these problems depends on routine plant inspections. Acting quickly will help to considerably raise plant health and productivity.
The Role of Nitrogen in Cannabis Growth
The cornerstone of cannabis plant health is nitrogen, which is important for a variety of physiological functions:
- Protein Synthesis: The amino acids that make up proteins, which are the building blocks that accelerate cell development and repair, rely on nitrogen.
- Chlorophyll Production: The production of chlorophyll, a pigment that is essential to photosynthesis, depends on nitrogen.
- Genetic Material Formation: Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, which are required for cell function and reproduction, need nitrogen.
Cannabis plants struggle to develop, produce fewer yields, and become less resilient to shocks when they don’t get enough nitrogen. Providing a balanced nutrient regimen ensures robust, healthy plants.
Identification of Cannabis Plant Nitrogen Deficiency
Maintaining the health of plants relies on early diagnosis of nitrogen shortages. In order to diagnose the problem, it is crucial to distinguish between nutrient deficits and analyze leaf symptoms.
A number of indicators should be employed to assess nutritional deficits in cannabis plants:
- Examine the Lower Leaves: The first to experience a nitrogen deficit are typically older, lower leaves.
- Changes in Color: Deep green leaves indicate health. The tips of these leaves turn yellow when there is a nitrogen shortage.
Though they are often accompanied by other symptoms such as browning edges or interveinal chlorosis, deficiencies in potassium or magnesium can also cause yellowing.
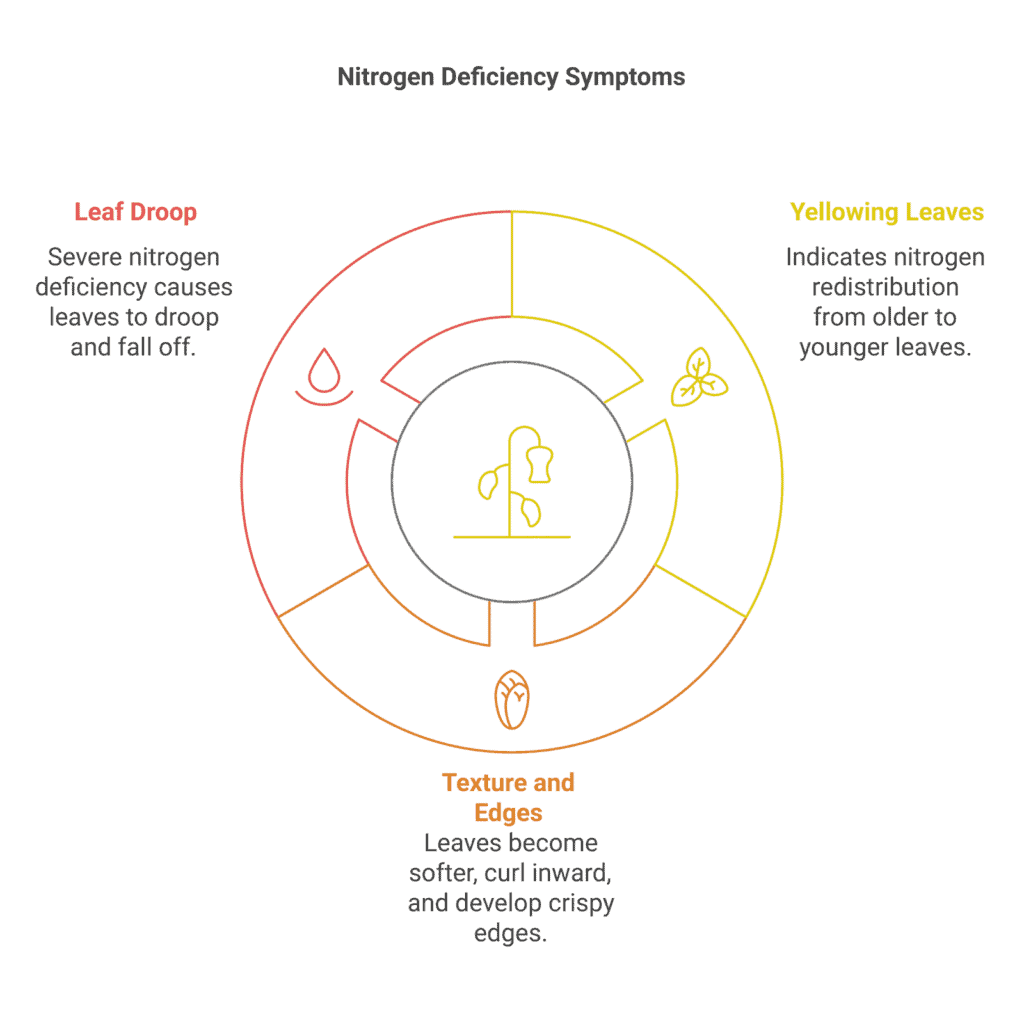
Understanding Leaf Symptoms
Leaves are an essential indicator of a nitrogen deficit:
- Yellowing Leaves: The plant causes the yellowing by redistributing nitrogen from older leaves to younger growth.
- Texture and Edges: The leaves may get softer, curve inward, and have golden, crispy edges.
- Leaf Droop: Indicating a serious deficit, afflicted leaves may droop and eventually fall off.
By spotting these indicators early on, you may take action and effectively restore the health of your plant.
Addressing the Lack of Nitrogen
Applying the proper fertilizers, adjusting the soil’s pH, and keeping an eye on plant reactions are all necessary to restore the nitrogen deficit. Nitrogen can be obtained from both organic and inorganic sources to enhance plant growth and health.
Modifying Nutrient Solutions and Soil pH
Nitrogen is best absorbed by cannabis plants in soil that has a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. A pH outside of this range hinders the intake of nutrients.
- Reduce pH by adding sulfur or acidic additives.
- Applying alkaline or lime additions will elevate the pH.
Additionally, a well-balanced nutrient solution is essential. Choose water-soluble fertilizers that are specifically designed for cannabis and contain enough nitrogen and other vital elements. Carefully stick to dosing requirements to avoid overfertilization.
Sources of Nitrogen – Organic and Inorganic
One can obtain nitrogen from both organic and inorganic sources:
- Organic Sources: Fish meal, blood meal, and compost are examples of organic sources that promote soil health and microbial activity while releasing nitrogen gradually.
- Inorganic Sources: A quick boost in nitrogen is provided by urea or ammonium nitrate.
When fertilizing, keep a watchful eye on your plants to avoid overfeeding, and modify feeding schedules as necessary.
Nitrogen Requirements During Growth
The stage of cannabis growth determines the amount of nitrogen required. Toxicology and deficiency must be avoided with proper management.
Nitrogen Requirements for Flowering and Vegetative Stages
When plants focus on producing leaves and stems during the vegetative stage, their demands for nitrogen reach their peak. Poor yields and stunted growth can result from a deficit during this time.
During flowering, lowering nitrogen levels will encourage the growth of buds. Excess nitrogen at this point can reduce the quality of the buds and postpone blossoming. Switch to a bloom fertilizer that has less nitrogen and more potassium and phosphorus.
Preventing Toxicity and Insufficiency
- Keep a balanced feeding schedule to avoid nitrogen deficiency during vegetative growth.
- To get the most out of fertilizer, regularly check the pH and moisture content of the soil.
- To avoid nitrogen toxicity, apply fertilizers sparingly.
- Look for dark green leaves with clawed tips, as these are frequently a sign of toxicity.
- Rinse the soil with water to remove excess nutrients if the soil is toxic.
Complex Topics in Deficiency in Nitrogen
For sophisticated cannabis growing, it is crucial to comprehend how plant physiology and nutrient absorption interact.
Plant Physiology and Nutrient Interactions
For photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and general plant health, nitrogen is essential. When there is a nitrogen shortage, resources are reallocated, with older leaves giving up nutrients to support new growth.
The roots are necessary for the absorption of nutrients. Deficits can be made worse by poor root health, which will impact plant growth and yield. Balance is maintained and healthy plant development is encouraged with routine soil testing and nutrient monitoring.
Increasing Uptake of Nutrients
In order to maximize nutrient uptake, soil management is necessary.
- Make sure that drainage and aeration are enough to sustain robust root systems.
- The ideal pH range for soil is 6.0 to 7.0.
- Make use of fish emulsion or blood meal, which are organic additives that release nitrogen gradually.
These methods boost the health of the plants as well as their capacity for growth and yield.
In Conclusion
A prevalent but controllable problem in cannabis cultivation is nitrogen shortage. Growers can rapidly restore plant health by being aware of its signs, causes, and treatments. A balanced nutrition regimen throughout the development cycle assures healthier plants, bigger yields, and cannabis of better quality. Successful harvests depend on proactive management and routine observation.








