Key Takeaways
- Heirloom strains are stable genetically and remain consistent through generations.
- Natural mutation or human interference might lead to mutant strains, which have specific characteristics.
- GMO seeds allow the incorporation of certain genes for traits such as disease resistance, and hybrids combine such traits using breeding.
- For any cannabis strain improvement, selective breeding is essential. It helps keep track of the yields, potency, and resilience of the strain.
The genetics of cannabis is important when it comes to growing cannabis plants, whether they are classic heirloom strains or newer mutant strains. Mutant strains are known to have distinct characteristics and a high potential for versatility, while heirloom varieties are adored by many due to their stable nature and rich history. Their differences are something all growers and breeders need to take note of, especially in today’s dynamic cannabis world. This article will delve into the science of these strains and explain their features and how they are impacting modern-day cannabis growing techniques.
What Are Mutant Strains and Heirloom Strains in Cannabis Genetics
Heirloom strains can be described as a breeding type that encapsulates unique features and traits due to its wide-scale open breeding. Mutants, on the other hand, utilize intentional crossbreeding to capture certain unique characteristics.
Understanding Heirloom Varieties: What Does It Mean to Breed True?
Cannabis heirloom strains are perhaps the most stable due to their genetic constitution and the genetic traits that each strain exhibits. “Breeding true” is the process where a strain reproduces itself when grown from seed. This is mostly done by open pollination with the help of non-associated animals or people for genetic change to the plant. These varieties have immense value because they are consistent in terms of yield, potency, flavor, and health of the plant.
The Origins of Mutant Strains: A Natural or Induced Phenomenon?
Two main factors that give rise to mutant strains of cannabis is genetic drift and breeding procedures that are performed on them. These features can also bring about physical changes like distinct bud forms, changes in leaf shape, or changes in the way the strain affects the user. Some of those mutations emerge spontaneously because of recessive gene variants or due to some environmental pressures. Further, breeders can introduce targeted mutations to achieve certain characteristics, like increased THC levels or greater disease resistance.
Key Characteristics of Heirloom and Mutant Strains

How Do Heirloom Seeds Differ from GMO Seeds
Heirloom seeds retain their genetic and disease resistance due to the open pollination process.
The Role of Open Pollination in Heirloom Strains
Open pollination is simply the process of moving pollen from one flower or plant to its counterpart and is accomplished using the wind, bugs, and other elements of nature. To preserve the genetic spectrum while growing the cannabis plant in different environments, the plant is cross-pollinated.
Heirloom strains are dependent on cross-pollination so their traits remain unchanged throughout the generations. With time, the plants’ environments aid in creating heirloom strains that have disease and pest resistance.
GMO Varieties: Inserting Genes vs. Selective Breeding
A genetically modified organism is an organism whose genetic composition has been altered through direct imposition of genes to attain certain characteristics. In the case of cannabis, such characteristics may include enhanced disease resistance, pest resistance, or greater growth and potency in the plant’s genome.
On the other hand, selective breeding entails selecting parent plants with those characteristics naturally, so that the offspring produced are not modified but retain the parent traits.
Disease Resistance and Yields: A Comparison
GMO cannabis varieties are designed to be disease-resistant, as they often contain genes that serve to boost immunity against certain diseases. Meanwhile, non-modified cannabis, such as heirloom strains, can naturally acquire disease resistance from cross-pollination and reproduction. As a result, heirloom strains can evolve to suit their ecological niche.
Further, GMO strains are developed for impressive yields, while the heirloom variants’ yields are comparatively less impressive but more dependable and of superior quality. The grower’s preference would help determine which strains to get.
Hybrid Seed vs. Pure Strains: What’s the Difference?
Hybrid seeds tend to outperform their parents in terms of growth rate, potency, yield, as well as disease resistance. This vigor, or heterosis, happens to the offspring when it is a cross between two different genetic strains. They also show up when cannabis seeds are bred out of two genetically different cannabis plants.
However, hybrids get to have genetic backgrounds from both parents, which helps when crossbreeding so they can grow stronger and more productive cannabis plants. On the other hand, hybrids can perform well in a variety of different conditions, while pure strains are consistent.
Sativa Dominant Strains and Their Unique Traits
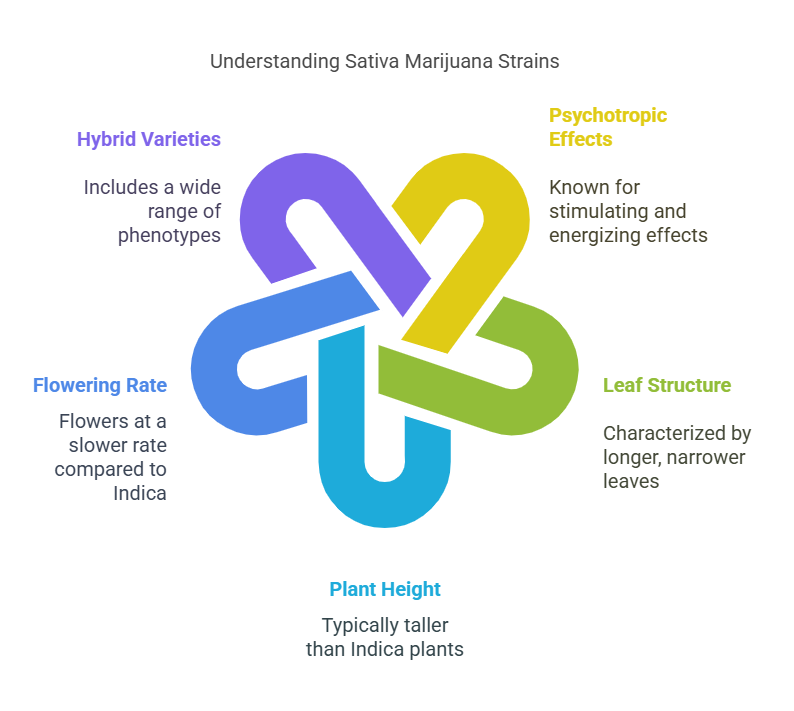
Sativa marijuana strains are well known for their psychotropic effects which are mostly stimulating. Their leaf structure tends to grow longer. Often, Sativa dominant plants tend to be taller than Indica plants, which typically flower at a quicker rate. Sativa dominant hybrids also have these characteristics but seed producers can select from a variety of strains to expand the variety of phenotypes available. Sativa-dominant hybrids are popular around the world due to their high levels of THC.
Can Hybrid Seeds Save Growers Time and Resources?
Hybrid seeds offer numerous advantages for cannabis growers, especially concerning time and resource consumption. The primary goal that hybrids achieve is hybrid vigor, meaning they would grow faster and stronger as compared to the pure strains. In most situations, this genetic advancement shortens the duration required to get to harvest and improves the plant’s tolerance to environmental stressors. Moreover, hybrids are more resilient to a wide range of conditions, aiding the grower in the management of their crops. These rewards are crucial to large-scale and commercial growers intending to boost productivity span.
The Science of Selective Breeding in Cannabis
How Growers Enhance Traits for Modern Strains: Cannabis growers employ selective breeding to improve desirable traits in a strain, by choosing the best-performing parent plants. This is also applicable for a breeder who chooses to cross plants that already have high THC content, are more resistant to disease, and also have a faster flowering time so that the offspring inherits those traits.
As mature plant generations are bred, the desired characteristics will become more refined and stable, giving rise to modern strains that are suited for a specific breeder or consumer’s purpose. These growing parameters make growers capable of meeting ever-changing needs in the recreational and medical cannabis markets.
Recessive Genes and Phenotypes: Recessive genes are very important in cannabis since they contribute to the phenotype of the cannabis plant. An individual must inherit a recessive gene from both parents to express that particular trait. For example, a plant thet has a recessive gene for a certain color of bud or an irregular leaf shape is likely to go unnoticed unless it is crossed with another plant that also possesses the same recessive trait. To some extent, it is acceptable to intercross plants of the same type because they can predict and select certain traits for future generations.
The Role of Generations in Refining Genetic Lines: Multiple generational breeding of cannabis is necessary for attaining desired plant traits and pure lines of plants. As breeders select plants based on desirable characteristics, they can improve their genetic lines and obtain consistent results with subsequent retail crops. During this multi-generational process, the genetic base of the strain is enriched, making the obtained plants more stable. In the long run, this generates cannabis strains that not only have a particular set of features but can be retained and relied upon in the future.
Are Heirloom Strains Better Than Modern Strains
Heirloom cannabis is rich in culture and historically significant but comes with lower yields and lacks the traits offered by hybrids.
Pros and Cons of Heirloom Varieties
Heirloom cannabis strains are highly regarded for their genetic stability and authentic characteristics, which guarantee good results for the growers. Compared to modern hybrids, heirloom strains are often low-yield and have low resistance to pests and diseases. Increased environmental pressures due to shocks can render heirloom strains infeasible. While they are of great historical and culture-specific importance, heirlooms require significantly more work as compared to modern cannabis varieties.
Modern Strains: Best Traits vs. Authenticity
Specific characteristics such as high percentages of THC, a short flowering period, and great flavor can be found in modern cannabis strains that are bred for said traits. Due to hybrid vigor, this group yields a higher output while remaining versatile with environmental change. However, traditional cannabis genetics lose their purity and authenticity. The blueprint characteristics of heirloom varieties are often not present within modern strains, as they only focus on meeting contemporary demands.
Breeders face a challenge in integrating cannabis heirlooms with modern-day genetics. By developing hybrids of heirlooms with new genetics, they can preserve the best aspects of both worlds simultaneously. This has allowed breeders to establish modern hybrid strains with advanced stability and performance characteristics. In doing so, a strong connection is preserved between the cultural history of cannabis and the future endeavors of breeding.
Conclusion
Understanding cannabis genetics is vital for growers and breeders aiming to produce according to market demands while maintaining the integrity of the plant. While venturing into heirloom or mutant designs, the primary focus has to firmly be achieving a middle ground between authenticity, innovation, and sustainability. Taking insights from other crops and adopting modern breeding methods would yield a dependable and diverse cannabis industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between heirloom and mutant strains
Heirloom strains do not lose their genetic originalization, whereas mutant strains happen either naturally or through genetic modifications, leading to an alteration.
Are GMO seeds better than heirloom seeds for cannabis cultivation
GMO seeds have the benefits of providing immunity against diseases and achieving maximum productivity. However, these do not possess the genetic variations and natural adaptability that heirlooms possess.
Why are hybrid seeds popular among growers
Hybrid seeds combine the outstanding features of two strains, which increases yield production and increases the resistance and adaptability of the hybrid over the pure ones.
How does selective breeding enhance cannabis strains
Selective breeding techniques enable growers to select favorable traits like high potency, appealing flavors and resistance so any particular strain can be refined and modified over several generations.








