
Key Takeaways
- Phytocannabinoid compounds are extracted from cannabis plants and assist marijuana consumers in rendering mood disorders and pain related inflammation issues.
- When using these compounds, some are stronger than others. THC is potent and used to impact people's perceptions. CBD is used to treat chronic pain and deal with inflammation issues.
- Phytocannabinoids are plant-based, making them safer to use than synthetic cannabinoids, which are stronger and more dangerous.
THC and CBD contain neural therapeutic components that can help in adjusting an individual’s emotions and reducing the feeling of pain as well as inflammation. Yet another wondrous gift from nature, phytocannabinoids are already serving as an aid in so many medical issues. Phytocannabinoids seem to have incredible potential and in this article we will mainly focus on their specific functions and applications in health and medicine alongside cannabis.
What Are Phytocannabinoids
Phytocannabinoids are the primary components found in cannabis plants in different strains and subspecies[1].
Key Differences Between Natural and Synthetic Cannabinoids
Firstly natural compounds derived from cannabis, for example, THC and CBD, are safe to consume, as well as effective in dealing with pain and inflammation.
On the other hand, synthetic cannabinoids are made from chemically composed materials that act like cannabinoids and have a chance of being more efficient. Their potential of being more efficient becomes a disadvantage, as they have a selective binding which is more potent.
The Role of Phytocannabinoids in Human Biological Systems
How Do Phytocannabinoids Work in the Human Body
Phytocannabinoids are capable molecules present in the human body which interact with specialized cells and other organs of the body.
Cannabinoid Receptors (CB1 and CB2) and Their Functions
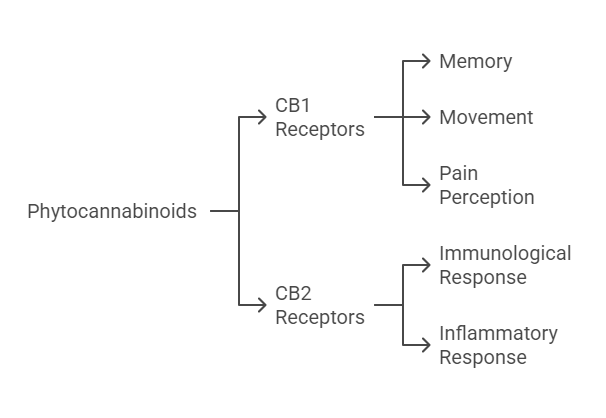
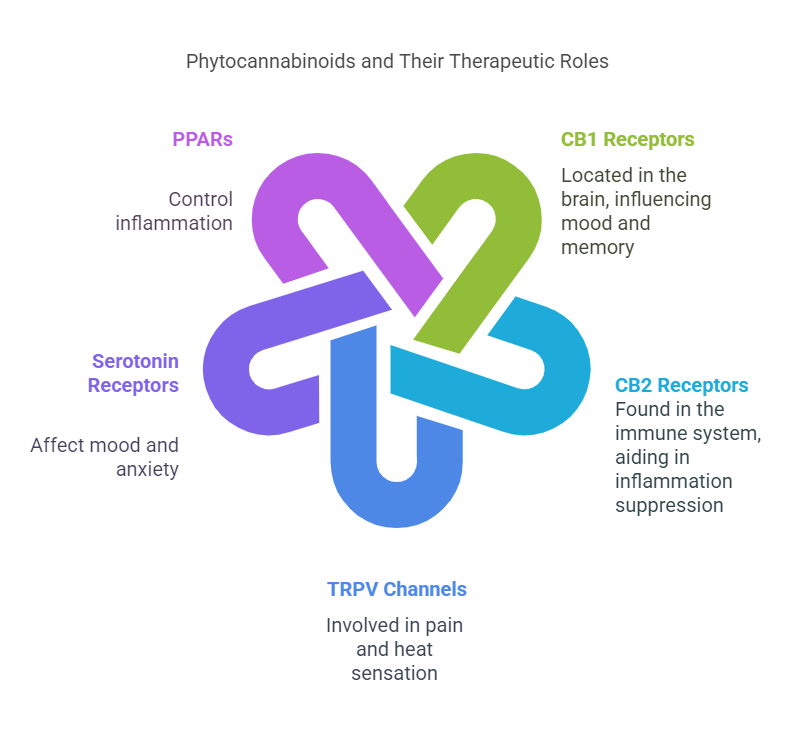
Phytocannabinoids can interact with particular ligand binding sites located within the human organism. Two major types exist, CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are present in muscle structures and the nervous system. These receptors enhance memory, mobility, and pain perception. CB2 are the immune system receptors that respond to inflammatory or immunological triggers.
Unlike THC which is only active at the CB1 receptor, CBD is active at both CB1 and CB2 receptors. THC is a hallmark of some phytocannabinoids to have a CB1 receptor preference. There are Several receptors with higher estrogen and THC affinities.
Interaction Between Phytocannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system has endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes and other substances which aid in body functioning. The major rationale of inclusion of phytocannabinoids into the endogenous system is to augment or suppress some of its antagonistic actions. This justifies the application of inscribed phytocannabinoids as tokens of endocannabinoids that are discharged to maintain equilibrium[2].
or example, if the body anticipates CBD to reduce the concentrations of the deactivating enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase, it will prevent the metabolism of its own endocannabinoids. This way, the endocannabinoid substance can be held in the body for a much extended period of time.
Molecular Targets and Binding Affinity of Cannabinoids
CBD and THC, two common cannabinoids, have varying effector activity towards the cannabinoid receptors in the human body. The CB1 receptor status-activating partial zeithamtharics, of which THC is one, has high occupancy to THC. Occasional low levels of time-binding efficacy have made CBD largely non-selective, passive, and willing to interact with indirect receptors as well as other molecular targets. Further, CDP acts on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and contains anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective tendencies.
What Are the Therapeutic Properties of Phytocannabinoids

Marijuana users tend to enjoy several therapeutic effects while recreationally using phytocannabinoids.
Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Effects
Phytocannabinoids are well known to be analgesic and anti-inflammation agents. They can reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines through CB2 receptors, as observed with cannabidiol or CBD. Such effectiveness may be beneficial in the pharmacotherapy of various conditions, such as inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis and pain caused by inflammation.
Potential in Treating Neurological Disorders
The use of Cannabis has shown positive results for managing MS and Epilepsy related issues. Multiple sclerosis-related spasticity can be controlled using a combination of THC and CBD, as it helps reduce muscle stiffness and pain. This is associated with CB1 receptor interaction located in the nervous system.
Appetite Regulation and Cancer Treatment Applications
Cannabis patients diagnosed with cancer take THC to help with vomiting caused by chemotherapy and also to increase appetite post-treatment. The constant search into cannabinoids has revealed their ability to encourage apoptosis. Cancers can be managed through cell death by encouraging cannabinoids.
Exploring the Differences Between Cannabis Sativa and Its Subspecies

Cannabis differs from its subspecies and strains in various ways.
Chemical Constituents Across Cannabis Strains
Different cannabis strains and subspecies have different cannabis molecule content, and as such, some molecules are present more than others. For example, the cannabis sativa subsp indica generally bears an impressive amount of sedating cannabinoids, like cannabinol (CBN), in comparison to the cannabis sativa subsp sativa, which is more inclined towards THC.
Classical Cannabinoids Versus Tetrahydrocannabinol Derivatives
Cannabinoids like THC, CBD, and cannabinol are classified as classical cannabinoids as they are obtained directly from a cannabis source. However, tetrahydrocannabinol derivatives are molecules that are chemically modified to enhance their pharmacologic and therapeutic value with the aim of specific receptor-binding sites.
Aromatic Compounds and Essential Oils in Cannabis
Terpenes are other sources of cannabis, which is aromatic and has therapeutic potential. The combination of terpenes with essential oils also supports the entourage effect, where different parts of cannabis serve different purposes and boost the overall efficacy.
How Are Phytocannabinoids Studied in Clinical Trials
The medicinal element of the cannabis industry relies heavily on high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). It assists researchers in separating and quantifying the quantity of a specific cannabinoid to avoid errors and to administer the right dosage in a clinical context.
As research and medical practice continue to grow and evolve, study-based investment in big-scale marijuana-based clinical trials suffers. This is not only because of how cannabis-based medicine is still branded as one side of the narcotic drug spectrum but also due to how there is stigma attached to the drug in various regions of the world.
Phytocannabinoids and Drug Development

Phytocannabinoids can serve as tools against various issues like inflammation and chronic pain as they can be used in drug design.
Cannabinoid Agonists and Inverse Agonism
Drugs derived from cannabis are known to be selective or inverse agonists at the CB receptors. Such a characteristic can access some pathways and treat chronic pain, inflammation, and degenerative diseases of the nervous system.
The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors
The action of phytocannabinoids can alter the function of PPARs nuclear hormone receptors engaged in gene transcription. This is because cannabis allows for receptor saturation, which opens up an opportunity for anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agents for developing new medications.
Development of Cannabinoid-Based Therapeutic Agents
In order to increase their industrial usage, cannabinoids are modified without compromising the drug's specificity. This is done so that the net clinical benefits can be increased with the negative side effects being reduced, thus making the drug more efficient and wholesome than medicine.
What Does the Future Hold for Phytocannabinoid Research
Research on phytocannabinoids has huge potential in both the medical and cannabis industries.
Advances in Synthetic Cannabinoid Production
Progress in the development of synthetic cannabinoids is very indicative of the creation of new substances with better receptor selectivity and greater affinity of receptor binding. Apart from allowing for new avenues in pharmacological research, these advances would improve the treatment of several diseases.
Potential Molecular Mechanisms for New Therapies
The involvement of anandamide in the cannabinoid action metabolic pathway has sparked the interest of a number of cancer bio scientists especially the endo cannabinoid metabolic enzymes and their interact cellular pathways. Such mechanisms help in the process of developing novel therapeutic approaches.
Expanding Applications for Inflammatory Pain and Beyond
Phytocannabinoids can be of help in relieving inflammatory pain and some forms of neuropathy and even prevent vomiting and nausea caused by the chemotherapeutic agents. Such developments underline and enhance the role of phytocannabinoids in clinical practice.
Conclusion
Phytocannabinoids can be explained as compounds from cannabis plants. Their application is popular because they are effective in treating joint inflammation and some mood imbalance disorders when combined with the human endocannabinoid system. Cannabis has been regarded for some time as a branch of science with low viability for commercialization, but the growing interest of multinational companies changes the narrative, and diseases that were previously incurable are potentially remediable. Thus, phytocannabinoids are of great importance in the development of cannabis and health care in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are phytocannabinoids?
Phytocannabinoids are plant substances or compounds that are obtained from the cannabis plants.
How do phytocannabinoids differ from synthetic cannabinoids?
Phytocannabinoids are derived from cannabis plant material, while synthetic cannabinoids can be made in labs.
What conditions can phytocannabinoids help treat?
Phytocannabinoids are mainly used to relieve chronic pain, fight inflammation, and help people with cancer deal with nausea.
Are there risks associated with phytocannabinoids use?
when you use phytocannabinoids, you are less likely to encounter dangerous risks. You may, however, have side effects like dizziness or fatigue if you lack proper guidance.
References
- Ladha, K. S., Ajrawat, P., Yang, Y., & Clarke, H. (2020). Understanding the medical chemistry of the cannabis plant is critical to guiding real world clinical evidence. Molecules, 25(18), 4042. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184042
- Ligresti, A., De Petrocellis, L., & Di Marzo, V. (2016). From phytocannabinoids to cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoids: pleiotropic physiological and pathological roles through complex pharmacology. Physiological reviews. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00002.2016
