Key Takeaways
- Synthetically produced CBD comes from laboratory synthesis, unlike the natural version, which is derived from hemp plants
- It plays a significant role in research.
- The legal status varies by state.
Synthetic CBD, a known derivative of synthetic cannabinoids, just may be the next best thing to traditional CBD. While both are therapeutic, the former is manufactured in labs. This guide covers everything about synthetic CBD and how it differs from its natural counterpart.
What is synthetic CBD?
Synthetic CBD is a lab-created compound designed to mimic the molecular structure and therapeutic effects of natural cannabidiol (CBD). It was created to address natural CBD challenges like contamination risks, legal restrictions, and inconsistencies in plant-derived products.
When comparing synthetic to natural CBD, you’ll note:
- Both have the same molecular structure; they interact with the body in identical ways.
- Synthetic CBD is scalable as it’s produced without the challenges of farming.
- Both deliver the same therapeutic effects.
- Some consumers prefer “natural” products, even though synthetic CBD is equally effective and often safer.
- Both affect the endocannabinoid system in the body similarly, working mostly as indirect modulators of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2).
How is Synthetic CBD Created?
Creating this synthetic cannabis product involves a series of complex chemical reactions. Here are the key steps:
- Select a Base Chemical: Scientists start with a chemical precursor, often derived from hydrocarbons, to form the foundation of the CBD molecule.
- Build the CBD Structure: Through a series of reactions, the molecular structure of CBD is assembled, ensuring it exactly matches the natural version.
- Purification and Testing: The final product is purified from impurities or byproducts. Rigorous quality testing meets pharmaceutical-grade standards.
Synthetic vs Natural CBD
While both aim to provide the same therapeutic effects, they differ.
| Aspect | Synthetic CBD | Natural CBD |
| Source | Lab-created using chemical synthesis. | Extracted from cannabis or hemp plants. |
| Purity | Highly consistent, with no plant-based impurities. | May contain trace amounts of other cannabinoids, terpenes, or contaminants. |
| Environmental Impact | It requires no farming and reduces land and water usage. | Relies on large-scale cultivation, which can impact the environment. |
| Cost | Production can be scalable and cost-efficient in the long run. | Cost depends on farming, extraction, and processing methods. |
| Legality | Often regulated differently, it can be more accessible in regions with cannabis restrictions. | Legal status varies based on the THC content and local cannabis laws. |
| Molecular Structure | Identical to natural CBD, ensuring similar biological effects. | Naturally occurring but can vary slightly depending on the plant strain. |
| Production Time | Produced on-demand in controlled lab settings. | Dependent on the cannabis/hemp plant growth cycle. |
| Contaminants | Free from molds, pesticides, and heavy metals. | Risk of contaminants if plants are grown in poor conditions or not properly tested. |
| Public Perception | Viewed as “unnatural” by some consumers. | Generally perceived as a more natural and holistic option. |
| Applications | Mainly used in pharmaceuticals as well as in research. | Has been adopted into various products, including drugs and recreational products. |
Benefits of Synthetic CBD
Synthetic CBD has several advantages that make it a preferred option:
- Consistency: Laboratory production ensures each batch has the same purity and potency, avoiding variations common in plant-derived CBD.
- It provides a legal and reliable alternative where cannabis cultivation is prohibited.
- It is free from contaminants like pesticides that may be present in plant-based products.
- It reduces the environmental footprint associated with cannabis cultivation.
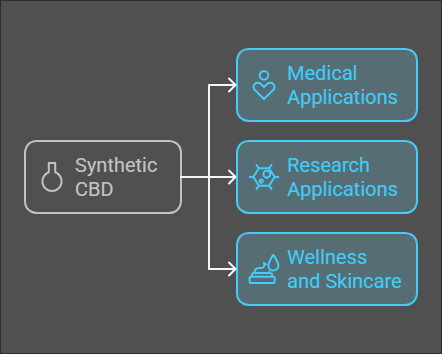
What Are the Uses of Synthetic CBD?
Synthetic CBD is finding applications in various fields:
Medical Applications
This synthetic marijuana product has new frontiers in the world of medicine. It’s being studied for its possible use in treating chronic pain, epilepsy, and anxiety. Researchers are keen on modifying synthetic CBD to attach to certain receptors in the brain.
Research Applications
Synthetic CBD is crucial in research due to its purity and consistency. Researchers can study its effects without the variability introduced by other compounds present in natural extracts. This is particularly important in researching the specific effects of CBD on the body.
Wellness and Skincare
CBD is popular in the health/wellness world for relaxation, better sleep, and easing discomfort. Consequentially, tinctures, gummies, and CBD-infused supplements sell out. In skin care, CBD is loved for its anti-inflammatory/antioxidant benefits, which help calm irritation, reduce redness, and fight signs of aging.
Legal Landscape
Regulations vary widely. In the U.S., the 2018 Farm Bill legalized hemp-derived CBD containing less than 0.3% delta-9 THC. However, synthetic CBD doesn’t fit this bill. Globally, the legal status is mixed. While some embrace it for its potential benefits, other states remain cautious, citing safety and ethical concerns.
The Endocannabinoid System and Synthetic CBD
Like natural CBD, synthetic CBD also interacts with the endocannabinoid system, ECS. This controls mood, sleep, appetite, immune response, and pain. Here’s how synthetic CBD interacts with it:
1. Binding to Receptors
The ECS has two primary receptors:
- CB1 receptors: in the brain and central nervous system.
- CB2 receptors: in the immune system and peripheral tissues.
Just like natural CBD, the synthetic one doesn’t directly bind to these receptors. Instead, it influences how other compounds interact with them, resulting in pain relief, reduced inflammation, or anxiety reduction.
2. Inhibition of FAAH Enzyme
Synthetic CBD can inhibit the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which breaks down anandamide. By inhibiting FAAH, synthetic CBD can increase levels of anandamide, enhancing its positive effects like mood regulation and pain relief.
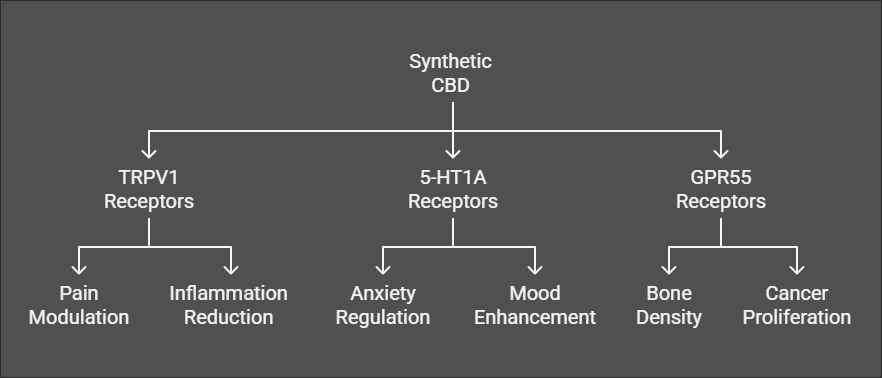
3. Modulation of Non-ECS Targets
In addition to ECS interaction, synthetic CBD also affects:
- TRPV1 receptors (involved in pain and inflammation).
- 5-HT1A receptors (serotonin receptors linked to anxiety and mood regulation).
- GPR55 receptors (has a role in bone density and cancer proliferation.)
4. Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects
Synthetic CBD influences cytokine production and other immune responses, contributing to its anti-inflammatory properties. It may also act as an antioxidant, protecting nerve cells from oxidative stress.
Safety Guidelines
Consider:
- Treat yourself to a very small dose and check how your body reacts.
- Before starting this synthetic cannabinoid, discuss any medications or supplements you’re on with your doctor.
- Always buy from a vendor you trust.
- Review dosage instructions and any warnings.
- Keep away from children and pets in a cool, dark place.
- Avoid going against local laws and regulations.
- Never combine synthetic cannabinoids with alcohol or recreational drugs. This may affect the central nervous system and create drug and alcohol dependence.
Conclusion
Synthetic CBD offers a promising alternative to natural CBD with its controlled production and potential for innovation. However, it’s essential to understand it fully to make informed decisions. Staying educated will help you navigate confidently and safely. Don’t forget to trip responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is synthetic CBD?
A synthetic cannabinoid meant to mimic the effects of CBD found in cannabis plants.
Is synthetic CBD safe?
The safety depends on the manufacturing process and quality control. Always look for third-party lab testing when choosing.
Can it get you high?
No, since it doesn’t contain the psychoactive tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
What are the positive effects?
Though more research needs to be done in this particular field, the synthetic cannabinoid relieves pain and reduces anxiety, similar to natural forms.
Why choose synthetic over natural CBD?
Synthetic CBD offers reliable quality, no agricultural challenges, and is free from environmental contaminants.
Does synthetic CBD have negative effects?
The negative effects may include drowsiness, dry mouth, diarrhea, and changes in appetite. If you experience liver enzyme elevation or allergic reactions, seek immediate medical attention.









